Introduction
Navigating complex HR management and compliance becomes crucial as businesses expand domestically and internationally. Professional Employer Organizations (PEO), Employers of Record (EOR), and Umbrella Companies offer distinct solutions to simplify workforce management. This guide provides a clear, side-by-side comparison to help enterprise decision-makers select the most suitable option.
What is a Professional Employer Organization (PEO)?
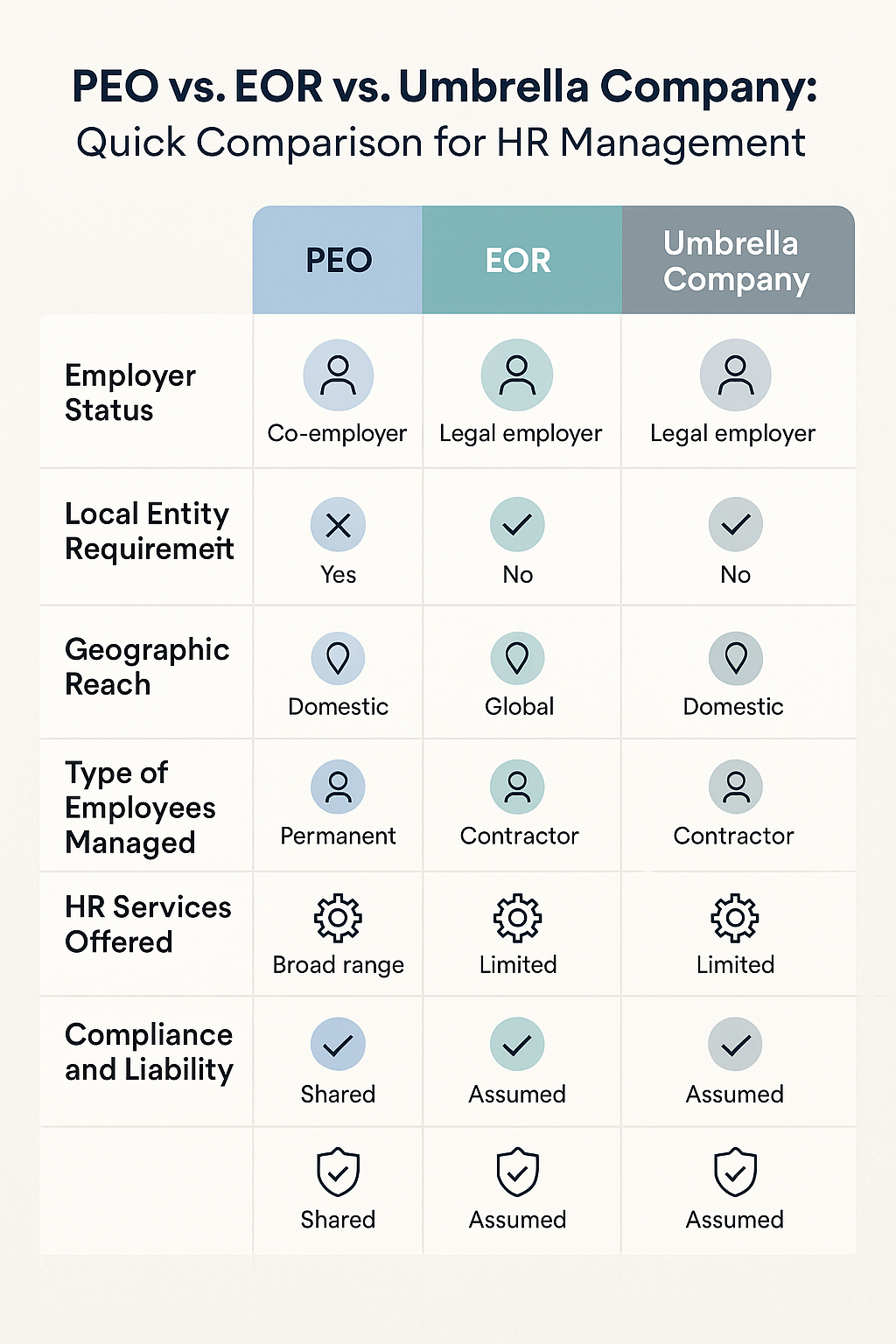
A Professional Employer Organization operates under a co-employment model, sharing employment responsibilities with your company, which must have an established legal entity in the region.
Key Features of a PEO
- Co-employment Structure: Shared responsibility for employees.
- Comprehensive HR Services: Payroll, benefits, compliance support, and HR consulting.
- Requires Local Entity: Only operates where your business is legally registered.
Example Use Case
A growing tech firm in the US partners with a PEO to manage HR administration, streamline payroll across multiple states, and offer competitive employee benefits packages.
What is an Employer of Record (EOR)?
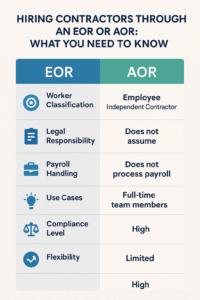
An Employer of Record acts as the full legal employer on your behalf, ideal for companies expanding internationally without local entities.
Key Features of an EOR
- Legal Employer: Full responsibility for compliance and legal employment obligations.
- No Local Entity Needed: Supports hiring in locations without local business registration.
- Global Reach: Effective for rapid international workforce expansion.
Example Use Case
A Canadian enterprise quickly hires employees in Brazil and Germany through an EOR, enabling them to start operations swiftly without forming foreign subsidiaries.
What is an Umbrella Company?
An Umbrella Company serves as the administrative employer for independent contractors, primarily handling payroll and tax compliance.
Key Features of an Umbrella Company
- Payroll Processing: Manages invoicing and contractor payroll.
- Compliance Management: Ensures tax and social contributions are accurately withheld.
- Limited HR Services: Focuses primarily on contractor payroll, not broader employee management.
Example Use Case
A UK consultancy firm engages contractors on short-term projects via an Umbrella Company to simplify payroll and tax compliance under IR35 regulations.
Side-by-Side Comparison
| Aspect | PEO | EOR | Umbrella Company |
|---|---|---|---|
| Employer Status | Co-employer | Sole legal employer | Administrative employer (contractors only) |
| Entity Requirement | Local entity required | No entity needed | No entity needed |
| Geographic Reach | Primarily domestic | International/global | Typically single-country |
| Scope of Employees | Full-time/part-time employees | Employees globally | Contractors/freelancers |
| HR Services | Comprehensive HR administration | Full employment compliance | Payroll and basic compliance |
| Liability | Shared | Full responsibility (EOR) | Tax and payroll compliance |
| Cost Structure | Percentage or flat per-employee | Typically flat per-employee fees | Weekly/monthly margin or flat fee |
Historical and Published Data
According to NAPEO, companies using PEOs experience faster growth and lower turnover, highlighting the strategic advantage of outsourcing HR functions. The global EOR market, valued around $5 billion in 2024, is growing rapidly due to increased remote and international employment trends.
Pros and Cons
Professional Employer Organization (PEO)
- Pros: HR expertise, enhanced benefits, cost-effective at scale.
- Cons: Requires local entity, shared compliance liability.
Employer of Record (EOR)
- Pros: Rapid global hiring, full compliance coverage, no entity required.
- Cons: Less direct control, potentially higher costs at scale.
Umbrella Company
- Pros: Simplifies contractor payments, reduces administrative burden, ensures tax compliance.
- Cons: Limited HR services, primarily for short-term engagements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
When should a company use an Umbrella Company?
Umbrella companies are ideal for managing independent contractors or freelancers, particularly in regions with complex contractor taxation, like the UK’s IR35.
Can a company use all three solutions simultaneously?
Yes. Many enterprises use a combination of PEO domestically, EOR internationally, and umbrella companies for contractor management.
Is using an EOR or Umbrella Company legally compliant?
Yes, reputable EOR and umbrella companies operate fully within local laws, ensuring compliance and reducing risks for client companies.
What’s the key difference between PEO and EOR?
The critical difference is employer status: a PEO shares responsibilities, while an EOR fully assumes employer obligations.
Conclusion
Choosing between a PEO, EOR, and Umbrella Company depends on your business needs, geographic presence, employee types, and strategic goals. Use PEOs for established domestic operations, EORs for international expansion without local entities, and umbrella companies to manage short-term contractors compliantly. Combining these solutions effectively can simplify HR processes, enhance compliance, and support sustainable growth.
Need help improving your hiring process? Contact Divino Solutions today for science-backed recruitment solutions or check out how to simplify recruitment or The Bias of Interviews: Are You Just Hiring a Smile?
Sources
- National Association of Professional Employer Organizations (NAPEO)
https://www.napeo.org - Velocity Global (EOR/PEO)
https://velocityglobal.com/resources/peo-vs-eor-whats-the-difference - Globalization Partners (Global EOR)
https://www.globalization-partners.com/employer-of-record-vs-peo-whats-right-for-your-company - Remote.com (EOR provider)
https://remote.com/blog/peo-vs-eor - U.S. Chamber of Commerce (Business & HR)
https://www.uschamber.com/co/run/human-resources/peo-vs-eor - Parasol Group (UK Umbrella Company and Contractor Management)
https://www.parasolgroup.co.uk/guides/what-is-an-umbrella-company - ContractorUK (Detailed explanations about UK umbrella companies)
https://www.contractoruk.com/umbrella_company - Brookson One (Umbrella Company solutions and contractor management)
https://www.brooksonone.co.uk/knowledge-centre/what-is-an-umbrella-company - Association of Independent Professionals and the Self-Employed (IPSE)
https://www.ipse.co.uk/umbrella-companies - EY (Ernst & Young) Report on Flexible and Contractor Employment
https://www.ey.com/en_uk/workforce/future-workforce-flexible-employment-models